FAQs
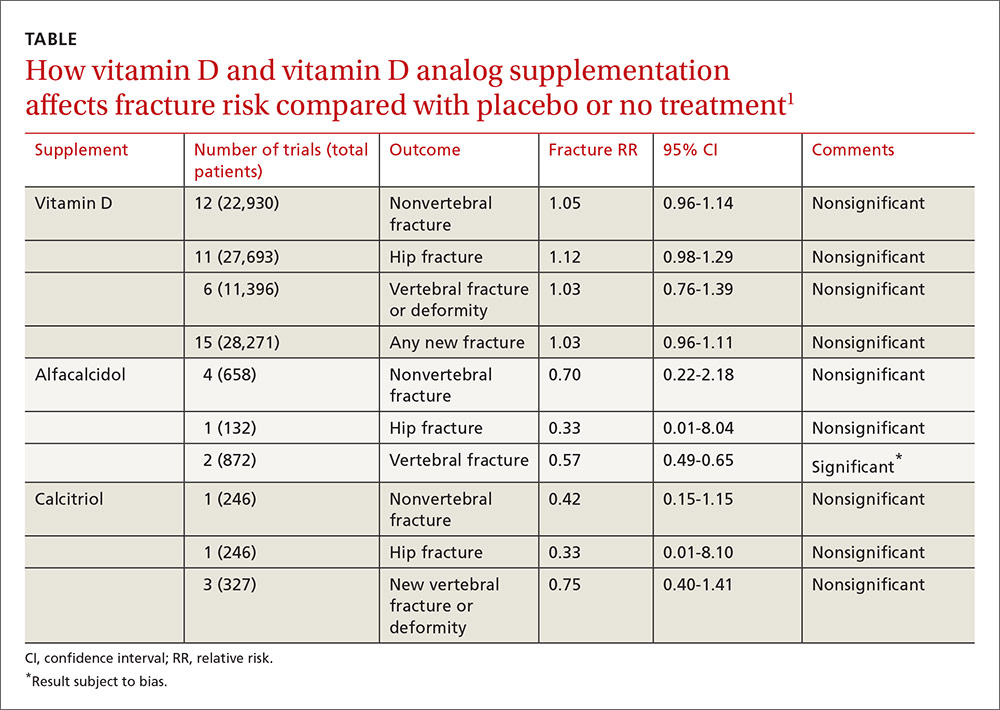
This relationship is biologically plausible. The results of 19 randomized clinical trials with vitamin D with or without calcium show varying results: a decreased fracture incidence in 7, neutral in 10 trials, whereas 2 trials with a high dose of vitamin D once per year showed an increased fracture incidence.
What happens if you take vitamin D without calcium? ›
Supplemental vitamin D without calcium—in doses averaging as much as 800 IU per day—doesn't reduce the risk of hip, vertebral, or nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women and older men (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, large, high-quality meta-analysis of randomized or quasi-randomized placebo-controlled ...
Does vitamin D reduce the risk of fractures? ›
Vitamin D3 reduced the rate of falls in a randomized-controlled trial (RCT) of postmenopausal women aged ≤ 65 years with osteoporosis23. These effects of preventing falls might be involved in the reduction of fracture risk.
Can consuming vitamin D and calcium reduce bone loss due to osteoporosis? ›
Vitamin D and calcium are essential for maintaining bone health, and their deficiency is an important risk factor for the development of osteoporosis [7]. Vitamin D is naturally produced in human skin upon exposure to sunlight.
Does calcium and vitamin D help fracture healing? ›
Studies performed in animal models have shown promising effects that adequate supplementation could enhance bone healing [7, 8]. From a biochemical aspect, vitamin D appears to be involved in every phase of the fracture healing process by mobilizing calcium.
Do you really need to take calcium with vitamin D? ›
Your body needs vitamin D to absorb calcium, but you do not have to take calcium and vitamin D at the same time. For the best absorption of calcium, make sure you get enough vitamin D. Vitamin D recommendations vary from province to province. Talk with your doctor about how much vitamin D you need.
Why is calcium no longer recommended? ›
On the other hand, recent studies have linked calcium supplements with an increased risk of colon polyps (small growths in the large intestine that can become cancerous) and kidney stones, which are hard masses usually formed in the kidneys from an accumulation of calcium and other substances.
What is the fastest way to increase bone density? ›
11 ways to increase bone density naturally
- Weightlifting and strength training. ...
- Eat more vegetables. ...
- Consume calcium throughout the day. ...
- Eat foods rich in vitamins D and K. ...
- Maintain a moderate weight. ...
- Avoid a low calorie diet. ...
- Eat more protein. ...
- Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
This could be due to increased bone resorption with suppressed secretion of parathyroid hormone (which is important for new bone formation). Previous studies have shown that high doses of vitamin D did result in increased resorption of bone unless calcium was also supplemented.
Do calcium supplements prevent fractures? ›
Indeed, the original recommendations for calcium supplementation were based on a study of elderly, nursing-home bound women with vitamin deficiencies and low bone density, for whom calcium and vitamin D supplements did significantly reduce fracture risk.
Calcium supplements can help repair damaged bones while strengthening them. In addition, vitamin supplements containing vitamin C, D and K can help bones heal faster.
How to speed up fracture bone healing? ›
There are several factors that can help to accelerate the healing of a fractured bone:
- Immobilization. Keeping the broken bone fragments in place is an essential factor in facilitating fast and safe healing. ...
- Nutrition. ...
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol. ...
- Physical Therapy.
Sunshine is a natural source of Vitamin D and 15-20 minutes of sunshine daily will boost your Vitamin D levels. Your doctor may recommend up to 5000u Vitamin D3 daily during periods of bone healing (available over-the-counter at your pharmacy). Like muscles, bones need exercise to stay strong.
What happens if you just take vitamin D? ›
Taken in appropriate doses, vitamin D is generally considered safe. However, taking too much vitamin D in the form of supplements can be harmful. Children age 9 years and older, adults, and pregnant and breastfeeding women who take more than 4,000 IU a day of vitamin D might experience: Nausea and vomiting.
Can too much vitamin D cause calcium loss? ›
Too much vitamin D can cause abnormally high levels of calcium in the blood. This can affect bones, tissues, and other organs. It can lead to high blood pressure, bone loss, and kidney damage if not treated.
Can you take vitamin D on its own? ›
Also, taking vitamin D alone or with calcium seems to improve bone density in people with existing bone loss caused by using corticosteroids. Weak and brittle bones (osteoporosis). Taking vitamin D3 by mouth along with calcium seems to help prevent bone loss and bone breaks in people with osteoporosis. Psoriasis.